ONLINE EXHIBITION From Earth to the Universe
A whole world of outstanding beauty at your fingertips
Cargando... Start
From Earth to the Universe
The beauty of the envolving Cosmos
Exhibition of astronomical images promoted by the International Astronomical Union and by the Andalusian Network for Technical and Scientific Public Outreach (RECTA) to commemorate the International year of the Astronomy.
Exhibition of astronomical images promoted by the International Astronomical Union and by the Andalusian Network for Technical and Scientific Public Outreach (RECTA) to commemorate the International year of the Astronomy.
From Earth to the Universe
The observable Universe appears full of galaxies
If you look at the Universe it appears full of galaxies to our eyes. The cluster of galaxies in Hercules contains 100 members of all kinds: elliptical, spiral and irregular galaxies.
If you look at the Universe it appears full of galaxies to our eyes. The cluster of galaxies in Hercules contains 100 members of all kinds: elliptical, spiral and irregular galaxies.
Cluster of galaxies in Hercules. 500 million light-years
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope / Coelum / J.C. Cuillandre & G. Anselmi
From Earth to the Universe
Usually galaxies gather in groups of moderate size…
The smallest groups of galaxies would have only two members. The pair known as “The Eyes” offers one example. Another group of galaxies is “Stephan´s Quintet”, containing only four members. The name is due to the presence of a fifth galaxy not belonging to the group, but interposed in the line of sight.
The smallest groups of galaxies would have only two members. The pair known as “The Eyes” offers one example. Another group of galaxies is “Stephan´s Quintet”, containing only four members. The name is due to the presence of a fifth galaxy not belonging to the group, but interposed in the line of sight.


The Eyes. 52 million light-years
Len Crawford (Rancho del Sol Observatory)
From Earth to the Universe
…or in clusters contining up to thousands of members
Apart from groups of galaxies such as the Hickson Compact Group 44 (made up of four galaxies), the so-called clusters of galaxies contain thousand of members. The combined gravitational attraction of such clusters is capable of bending the light coming from objects situated behind them. These further galaxies appear as light arclets. This phenomenon is known as gravitational lens.
Apart from groups of galaxies such as the Hickson Compact Group 44 (made up of four galaxies), the so-called clusters of galaxies contain thousand of members. The combined gravitational attraction of such clusters is capable of bending the light coming from objects situated behind them. These further galaxies appear as light arclets. This phenomenon is known as gravitational lens.


Gravitational lens in a cluster of galaxies. 5 billion light-years
M. Jee & H.Ford (NASA/ESA/JHU)
From Earth to the Universe
The variety of galaxies is astounding
The Universe harbours an astounding variety of galaxies with elliptical, spiral and irregular shapes. NGC 5128 is a peculiar elliptical system with a dusty lane across its centre caused by a collision with another galaxy. Common elliptical galaxies contain no dust. If you look at galaxy M106 you will see that it is a spiral system with a prominent nucleus surrounded by a disc containing several spiral arms.
The Universe harbours an astounding variety of galaxies with elliptical, spiral and irregular shapes. NGC 5128 is a peculiar elliptical system with a dusty lane across its centre caused by a collision with another galaxy. Common elliptical galaxies contain no dust. If you look at galaxy M106 you will see that it is a spiral system with a prominent nucleus surrounded by a disc containing several spiral arms.


Galaxy NGC 5128. 14 million light-years
Capella Observatory / Ciel et Espace
From Earth to the Universe
Our Galaxy belongs to the spiral type
Our Galaxy belongs to the spiral type, like NGC 7331. Spiral galaxies have a central bulge surrounded by a plane disc containing several spiral arms. You can see this shape clearly defined in the image of the Whirlpool Galaxy.
Our Galaxy belongs to the spiral type, like NGC 7331. Spiral galaxies have a central bulge surrounded by a plane disc containing several spiral arms. You can see this shape clearly defined in the image of the Whirlpool Galaxy.


The Whirlpool Galaxy. 31 million light-years
S.Beckwith (NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage Team)
From Earth to the Universe
The Magellanic Clouds are the closest galaxies to our own
The Magellanic Clouds (Large and Small) are two galaxies orbiting around our own. The are the closest stellar systems to us.
The Magellanic Clouds (Large and Small) are two galaxies orbiting around our own. The are the closest stellar systems to us.


Large Magellanic Cloud. 157.000 light-years
C. Smith, S. Points, Equipo MCELS (NOAO/AURA/NSF)
From Earth to the Universe
The Andromeda Galaxy is the largest in the Local Group
The largest member in the Local Group is the spiral in Andromeda. This galaxy has a central bulge made up from older and cooler stars, yellow in color, while the spiral arms inside the disc contain younger and hotter stars that shine with bluish hue.
The largest member in the Local Group is the spiral in Andromeda. This galaxy has a central bulge made up from older and cooler stars, yellow in color, while the spiral arms inside the disc contain younger and hotter stars that shine with bluish hue.
Andromeda Galaxy. 2,5 million light-years
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
Our Galaxy contains hundreds of billions of stars…
If you look at the centre of our Galaxy, you will perceive the huge quantity of stars that it contains. This area of the sky is situated towards the constellation of Sagittarius, in the southern celestial hemisphere. This part of the sky can be seen from almost any place in the world.
If you look at the centre of our Galaxy, you will perceive the huge quantity of stars that it contains. This area of the sky is situated towards the constellation of Sagittarius, in the southern celestial hemisphere. This part of the sky can be seen from almost any place in the world.
The centre of the Galaxy. 26.000 light-years
Janus Brink
From Earth to the Universe
…and immense clouds of gas and dust
When you look at the sky, beside Sagittarius, you can see the constellation of Scorpius with the reddish star Antares, one of the most luminous known. The river of light of the Milky Way shines at the left in this image, where stellar clouds intermix with clumps of gas and dust.
When you look at the sky, beside Sagittarius, you can see the constellation of Scorpius with the reddish star Antares, one of the most luminous known. The river of light of the Milky Way shines at the left in this image, where stellar clouds intermix with clumps of gas and dust.
Scorpius Constellation. 600 light-years to the brightest star
Stéphane Guisard
From Earth to the Universe
The Milky Way is the image offered by our Galaxy seen from inside
If you look at the sky on a dark night, you will see the Milky Way as a luminous band: it is made from accumulations of stars and nébulas in the plane of the disc of our Galaxy. This image displays the whole of the Milky Way, and is made up from photographs obtained in Germany and Namibia.
If you look at the sky on a dark night, you will see the Milky Way as a luminous band: it is made from accumulations of stars and nébulas in the plane of the disc of our Galaxy. This image displays the whole of the Milky Way, and is made up from photographs obtained in Germany and Namibia.
The Milky Way. 26.000 light-years
Eckhard Slawik
From Earth to the Universe
Clouds of dust and gas are called nebulas
In this image you can see several astronomical objects in the northern constellation of Cygnus. The brightest star is Deneb and to the left of it you have the North-America and Pelican nebulas: dust and gas clouds. Further down, to the right, beside the star Sadr, you can find the Buttterfly Nebula, one of the brightest regions in the Cygnus nebular complex.
In this image you can see several astronomical objects in the northern constellation of Cygnus. The brightest star is Deneb and to the left of it you have the North-America and Pelican nebulas: dust and gas clouds. Further down, to the right, beside the star Sadr, you can find the Buttterfly Nebula, one of the brightest regions in the Cygnus nebular complex.
Nébulas in Cygnus. 3.000 light-years to the brightest star
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
Nebulas are made up mainly of hydrogen
Other interesting nebulas are the Horsehead and other nebulosities in the Orion constellation, all of them composed mainly from hydrogen gas.
Other interesting nebulas are the Horsehead and other nebulosities in the Orion constellation, all of them composed mainly from hydrogen gas.


Horsehead Nebula. 1.500 light-years
Austral European Observatory (ESO)
From Earth to the Universe
Nebulas get condensed and stars are born inside them
These dust and gas clouds known as nebulas get condensed and stars are born inside them. You can see this process running in the Cone Nebula: in the upper part there is a very bright star, 5 Monocerotis, beside other recently formed objects. The Rossete Nebula shows a set of newly born stars at the very centre of the rose window.
These dust and gas clouds known as nebulas get condensed and stars are born inside them. You can see this process running in the Cone Nebula: in the upper part there is a very bright star, 5 Monocerotis, beside other recently formed objects. The Rossete Nebula shows a set of newly born stars at the very centre of the rose window.


Cone Nebula. 2.600 light-years
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
Stars are born in different sizes
The Eta Carinae Nebula lies in the constellation of Carina. Stars of all sizes are being born from these clouds. Especially outstanding among them is the star Eta Carinae, one of the most luminous yet known in the Galaxy.
The Eta Carinae Nebula lies in the constellation of Carina. Stars of all sizes are being born from these clouds. Especially outstanding among them is the star Eta Carinae, one of the most luminous yet known in the Galaxy.
Eta Carinae Nebula. 7.500 light-years
Capella Observatory / Ciel et Espace
From Earth to the Universe
Stars are born in groups
Stars are born in groups. You can see an example of these groups insde the Lagoon Nebula, a region of intense star-forming activity. The group of stars recently formed from these nebulosities bears the name NGC 6530. The energy from these stars lights up nebular hydrogen and makes it shine with reddish hues. One more star-forming region is the neightborhood of star cluster NGC 3603. This area contains one of the most outstanding groups of young stars in the Galaxy.
Stars are born in groups. You can see an example of these groups insde the Lagoon Nebula, a region of intense star-forming activity. The group of stars recently formed from these nebulosities bears the name NGC 6530. The energy from these stars lights up nebular hydrogen and makes it shine with reddish hues. One more star-forming region is the neightborhood of star cluster NGC 3603. This area contains one of the most outstanding groups of young stars in the Galaxy.


Lagoon Nebula. 5.000 light-years
Robert Jay GaBany
From Earth to the Universe
Stars born together build up a star cluster
Star formation starts when a gas and dust cloud gets condensed. Stars originate in groups, the so-called star clusters, like NGC 650. NGC 6250 was born 200 million years ago from the dark nebula Barnard 86.
Star formation starts when a gas and dust cloud gets condensed. Stars originate in groups, the so-called star clusters, like NGC 650. NGC 6250 was born 200 million years ago from the dark nebula Barnard 86.
Star cluster NGC 6520. 5.400 light-years
Gemini Observatory
From Earth to the Universe
There are young star clusters
The Universe offers to your sight young star clusters, like the Pleiades, or The Seven Sisters. This cluster is made up of young and hot stars. Greek mythology identifies its seven brightest members with the seven daughters of Atlas and Pleione.
The Universe offers to your sight young star clusters, like the Pleiades, or The Seven Sisters. This cluster is made up of young and hot stars. Greek mythology identifies its seven brightest members with the seven daughters of Atlas and Pleione.
Pleiades. 440 light-years
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
Young star clusters contain up to several thousands of stars
Young clusters contain up to several thousands of stars. This is the case of the Double Cluster in Perseus. These two clusters count among the most luminous, dense and closer star groups. It is believed that both were born from the same interstellar nebula some 13 million years ago. Young star clusters are also known as open clusters, of galactic clusters.
Young clusters contain up to several thousands of stars. This is the case of the Double Cluster in Perseus. These two clusters count among the most luminous, dense and closer star groups. It is believed that both were born from the same interstellar nebula some 13 million years ago. Young star clusters are also known as open clusters, of galactic clusters.
The Double Cluster. 7.500 light-years
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
There are old stars clusters too
The universe contains old star clusters too. NGC 6752 belongs to the group of old star clusters, in the southern constellation of Pavo. So does the Globular Cluster in Hercules, whose age exceeds ten billion years. Globular clusters are the oldest structures known to our Galaxy.
The universe contains old star clusters too. NGC 6752 belongs to the group of old star clusters, in the southern constellation of Pavo. So does the Globular Cluster in Hercules, whose age exceeds ten billion years. Globular clusters are the oldest structures known to our Galaxy.


Globular cluster in Pavo. 14.000 light-years
Anglo-Australian Observatory / David Malin
From Earth to the Universe
Hydrogen is transformed into other elements inside the stars
Stars have the same chemical composition as the nebulas from wich they were born: mainly hydrogen and helium. At stellar core, hydrogen is transformed into heavier elements through nuclear fusion reactions. The energy unleashed in the process comes out to the stellar surface and atmosphere. This ultraviolet image of the Sun shows the outermost layers of our star: the solar corona.
Stars have the same chemical composition as the nebulas from wich they were born: mainly hydrogen and helium. At stellar core, hydrogen is transformed into heavier elements through nuclear fusion reactions. The energy unleashed in the process comes out to the stellar surface and atmosphere. This ultraviolet image of the Sun shows the outermost layers of our star: the solar corona.
The solar corona. 8,3 light-minutes
Consorcio SOHO/EIT, NASA ESA
From Earth to the Universe
The Sun is a normal star…
The Sun is an ordinary star. It is situated at a distance of 8.3 light-minutes from our planet. In this image, obtained with the light emitted by hydrogen atoms, yo can perceive the details of the solar surface, also known as photoshphere.
The Sun is an ordinary star. It is situated at a distance of 8.3 light-minutes from our planet. In this image, obtained with the light emitted by hydrogen atoms, yo can perceive the details of the solar surface, also known as photoshphere.
The solar photosphere. 8,3 light-minutes
Greg Piepol
From Earth to the Universe
…and very quite compared to other stars
If you pay a closer look at the Sun, you will see sunspots. There are surface areas that become cooler tan their surroundings because the solar magnetic fields block the flux of energy coming from lower layers. Sunspots are the most conspicuous manifestation of solar activity. You can better appreciate the details of the solar chromosphere in images taken with ultraviolet light. The chromosphere is a solar layer placed between the visible photosphere and the corona. In the image you can witness a huge solar flare ejecting matter towards the outer atmosphere. This notwithstanding, the Sun is a rather quite star that displays a very constant enerby output.
If you pay a closer look at the Sun, you will see sunspots. There are surface areas that become cooler tan their surroundings because the solar magnetic fields block the flux of energy coming from lower layers. Sunspots are the most conspicuous manifestation of solar activity. You can better appreciate the details of the solar chromosphere in images taken with ultraviolet light. The chromosphere is a solar layer placed between the visible photosphere and the corona. In the image you can witness a huge solar flare ejecting matter towards the outer atmosphere. This notwithstanding, the Sun is a rather quite star that displays a very constant enerby output.
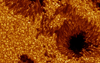

Sunspots. 8,3 light-minutes
G.Scharmer & K.Langhans, ISP. Image processing by por M.Löfdahl, ISP; Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
From Earth to the Universe
Solar activity affects the surroundings of our star
Coronal loops count among many different phenomena related to solar activity. These curved structures are bridges of solar matter at extremely hight temperature and electrically charged, that rise from the chromosphere and deepen into the solar corona. This material falls again, which causes an explosive solar flare known as coronal rain. Other manifestation of solar activity are ordinary solar flares, violent eruptions that appear around sunspots.
Coronal loops count among many different phenomena related to solar activity. These curved structures are bridges of solar matter at extremely hight temperature and electrically charged, that rise from the chromosphere and deepen into the solar corona. This material falls again, which causes an explosive solar flare known as coronal rain. Other manifestation of solar activity are ordinary solar flares, violent eruptions that appear around sunspots.

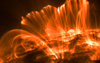
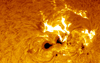
Coronal loops. 8,3 light-minutes
The TRACE Team at the space Research Institute Stanford-Lockheed, and NASA
From Earth to the Universe
The Sun is surrounded by giant planets such as Jupiter
Our star is surrunded by planets, ours among them. The largest planet in the Solar System is Jupiter. Observed with visible light, Jupiter shows brown and yellowish tones. But this image was obtained with infrared light and shows the height of different cloud formations: highest in white, médium in blue and lowest in red.
Our star is surrunded by planets, ours among them. The largest planet in the Solar System is Jupiter. Observed with visible light, Jupiter shows brown and yellowish tones. But this image was obtained with infrared light and shows the height of different cloud formations: highest in white, médium in blue and lowest in red.
Jupiter. 35 light-minutes
Telescope Gemini North, Travis Rector (U. Alaska Anchorage), Chad Trujillo and the Gemini Altair Team, NOAO / AURA / NSF.
From Earth to the Universe
Giant planets are composed of gas
In Jupiter you can see a Great Red Spot. It is a storm the size of the Earth, found in the southern hemisphere of that planet. Another giant planet is Uranus, third in size and seventh in distnce from the Sun. Giant planets consist mainly of gas. The green-bluish hue of Uranus is due to the absorption of red light by methane gas.
In Jupiter you can see a Great Red Spot. It is a storm the size of the Earth, found in the southern hemisphere of that planet. Another giant planet is Uranus, third in size and seventh in distnce from the Sun. Giant planets consist mainly of gas. The green-bluish hue of Uranus is due to the absorption of red light by methane gas.


The Great Red Spot. 35 light-minutes
California Association for Research in astronomy / Science Photo Library
From Earth to the Universe
Saturn is the most beautiful giant planet in the Solar System
Another giant planet you can see in the sky is Saturn, the most beautiful gaseous world in the Solar System. This image was taken by the space probe Cassini. In it you can see the shadows projected by the rings onto the northern hemisphere of the planet. Also, some stormy formations can be appreciated in the southern hemisphere.
Another giant planet you can see in the sky is Saturn, the most beautiful gaseous world in the Solar System. This image was taken by the space probe Cassini. In it you can see the shadows projected by the rings onto the northern hemisphere of the planet. Also, some stormy formations can be appreciated in the southern hemisphere.
Saturn. 71 light-minutes
NASA/ESA Cassini-Huygens
From Earth to the Universe
Small planets are of the rocky kind, like Mars…
Looking at the sky under the right circumstances, you will see the planet Mars, a rocky workd smaller than Earth. This image, taken by the space probe Mars Global Surveyor, shows clouds made of water ice crystals. Lower left there are clouds over the three volcanoes in Tharsis. The upper part shows the icy cover of the northern polar cap.
Looking at the sky under the right circumstances, you will see the planet Mars, a rocky workd smaller than Earth. This image, taken by the space probe Mars Global Surveyor, shows clouds made of water ice crystals. Lower left there are clouds over the three volcanoes in Tharsis. The upper part shows the icy cover of the northern polar cap.
Mars. 3 light-minutes
NASA/Mars Global Surveyor
From Earth to the Universe
…or the Earth sith its Moon
Another rocky planet is the Earth. This image displays the view over the Northern Atlantic. The view was generated with the software “Blue Marble” by NASA, a system that relays on images taken by several artificial satellites. Our planet has one natural satellite, the Moon, found at a distance of 1.25 light-seconds. The lunar landscapes show clear highlands and darker plains full of solidified magma known as the seas of the Moon (lunar maria). The lunar surface is covered by the scars left by meteoritic impacts: the lunar craters.
Another rocky planet is the Earth. This image displays the view over the Northern Atlantic. The view was generated with the software “Blue Marble” by NASA, a system that relays on images taken by several artificial satellites. Our planet has one natural satellite, the Moon, found at a distance of 1.25 light-seconds. The lunar landscapes show clear highlands and darker plains full of solidified magma known as the seas of the Moon (lunar maria). The lunar surface is covered by the scars left by meteoritic impacts: the lunar craters.


The Earth
Image generated by Reto Stöckli for the NASA GSFC Earth Observatory
From Earth to the Universe
Comets are tiny frozen worlds in the Solar System
Comets moving inside the Solar System are small icy blocks with sizes ranging from a few hundred metres (yards) to several kilometres (miles). When the solar radiation heats them up, the icy materials sublimate, and gases and dust are emitted, forming the cometary hair and tail. Examples of such objets are comet Machholz, C/2001 Q4, and comet Hale-Bopp.
Comets moving inside the Solar System are small icy blocks with sizes ranging from a few hundred metres (yards) to several kilometres (miles). When the solar radiation heats them up, the icy materials sublimate, and gases and dust are emitted, forming the cometary hair and tail. Examples of such objets are comet Machholz, C/2001 Q4, and comet Hale-Bopp.



Comet and Pleiades. 3 light-minutes
Jack Newton
From Earth to the Universe
Many stars are born with planets around them
Nebulas containing larger quantities of dust are prone to the birth of stars with planets around them. This is the case of those nebulas in the Corona Australis constellation, that appear as a large tail of shining interestelar dust lit up by nearby young stars. Aproximately one third fo the stars are surrounded by planets.
Nebulas containing larger quantities of dust are prone to the birth of stars with planets around them. This is the case of those nebulas in the Corona Australis constellation, that appear as a large tail of shining interestelar dust lit up by nearby young stars. Aproximately one third fo the stars are surrounded by planets.
Nebulas in Corona Australis. 500 light-years
Anglo-Australian Observatory / David Malin
From Earth to the Universe
Suns-like stars diet quietly
Helix nebula displays the shining envelope expelled by Sun-likes stars at the end of their existence. Sun-like stars die in a peaceful process that gives back to the interestelar médium part of the material that had been retained within the stellar interior.
Helix nebula displays the shining envelope expelled by Sun-likes stars at the end of their existence. Sun-like stars die in a peaceful process that gives back to the interestelar médium part of the material that had been retained within the stellar interior.
Helix Nebula. 690 light-years
NASA / ESA Hubble Space Telescope and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. C. R. O’Dell (Vanderbilt University) / M. Meixner y P. McCullough (STScI).
From Earth to the Universe
Other stars die in catacluysmic explosions
The Sun will have a quite ending, but other stars die in cataclysmic supernova explosions. Some supernovas leave behind compact objets called neutron stars. The energy emitted bu the neutron star found at the centre of the Crab Nebula makes the gas emit light and radio waves. Supernova explosions disperse into the interstellar médium huge quatities of heavy chemical elements produced from hydrogen inside the star throughout its stellar life.
The Sun will have a quite ending, but other stars die in cataclysmic supernova explosions. Some supernovas leave behind compact objets called neutron stars. The energy emitted bu the neutron star found at the centre of the Crab Nebula makes the gas emit light and radio waves. Supernova explosions disperse into the interstellar médium huge quatities of heavy chemical elements produced from hydrogen inside the star throughout its stellar life.


The Crab Nebula in radio. 6.000 light-years
M.Bietenholz (Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, HartRAO, & University of New York) for NRAO VLA
From Earth to the Universe
Stellar death enriches the Universe with heavy chemical elements
Supernova explosions are the only means by which the Universe is able to produce many of the chemical elements required for life. Nebula G292.0+1.8 was formed by a nearby supernova explosion some thousands of year ago. Tycho´s supernova remmant shows how the exploding material is expanding and becoming mixed with the interstellar medium. This matter gets incorporated into other nebulas.
Supernova explosions are the only means by which the Universe is able to produce many of the chemical elements required for life. Nebula G292.0+1.8 was formed by a nearby supernova explosion some thousands of year ago. Tycho´s supernova remmant shows how the exploding material is expanding and becoming mixed with the interstellar medium. This matter gets incorporated into other nebulas.

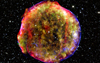
G292.0+1.8. 20.000 light-years
X-Ray image taken by S. Park and collaborators for NASA / Chandra X-ray Center and Penn State. Visible light image from the Digital Sky Survey.
From Earth to the Universe
Stars produce the elements needed for life, and contribute them to the Cosmos
The material expelled by the stars at the end of their lives is incorporated into interstellar nebulae and feeds the formation of new generations of stars and planets. Stars contribute the elmenets needed for life to the Cosmos. New stellar generations are born from material enriched with heavy chemical elements produced by stars that existed and disappeared a long time ago. The bright dot inside the darkest part of the Elephant Trunk Nebula is a newly-born star.
The material expelled by the stars at the end of their lives is incorporated into interstellar nebulae and feeds the formation of new generations of stars and planets. Stars contribute the elmenets needed for life to the Cosmos. New stellar generations are born from material enriched with heavy chemical elements produced by stars that existed and disappeared a long time ago. The bright dot inside the darkest part of the Elephant Trunk Nebula is a newly-born star.


Elephant Trunk Nebula. 2.400 light-years
Mischa Schirmer
From Earth to the Universe
Star-formatin processes are active in our Galaxy, and in others
Star formation is a current process in our Galaxy and in others. The Triangulum Galaxy shows signs of this. This galaxy is a spiral system whose arms appear sprinkled with pinkish nebulas that glow with the cahracteristic color of ionized hydrogen, the most outstanding tell-tale of current star formation. This galaxy is the third in size within our Local Group of galaxies.
Star formation is a current process in our Galaxy and in others. The Triangulum Galaxy shows signs of this. This galaxy is a spiral system whose arms appear sprinkled with pinkish nebulas that glow with the cahracteristic color of ionized hydrogen, the most outstanding tell-tale of current star formation. This galaxy is the third in size within our Local Group of galaxies.
Triangulum Galaxy. 3 million light-years
Robert Gendler
From Earth to the Universe
Star formation is more intense in colliding galaxies
When galaxies collide, intense star-forming processes are induced. You can see this clearly in the pair of colliding galaxies called The Antennae. The violent impact of gaseous masses compresses gas and causes intense starbursts. In the far fuure our Galaxy will collide with the Adromeda Galaxy.
When galaxies collide, intense star-forming processes are induced. You can see this clearly in the pair of colliding galaxies called The Antennae. The violent impact of gaseous masses compresses gas and causes intense starbursts. In the far fuure our Galaxy will collide with the Adromeda Galaxy.
The Antennae. 45 million light-years
NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team (STScl/AURA)
From Earth to the Universe
Each galaxy contains an immense multitude of stars
This image shows the centre of our Galaxy, seen in infrared light. More tan one million stars are registered inside this frame. The total number of stars in our Galaxy is around several hundred billion.
This image shows the centre of our Galaxy, seen in infrared light. More tan one million stars are registered inside this frame. The total number of stars in our Galaxy is around several hundred billion.
The galactic centre. 26.000 light-years
Telescopio espacial Spitzer. NASA/JPL-CALTECH/S.Stolovi (SSC/Caltech)
From Earth to the Universe
There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the observable Universe
The Hubble Space Telescope captures objects hundreds of millions of times fainter tan the dimmest star visible with the naked eye. This image contains more tan 10.000 objects, wich gives you an idea of the hundreds of billions of galaxies existing in our Universe.
The Hubble Space Telescope captures objects hundreds of millions of times fainter tan the dimmest star visible with the naked eye. This image contains more tan 10.000 objects, wich gives you an idea of the hundreds of billions of galaxies existing in our Universe.
Hubble Ultra-Deep Field. 13.000 million light-years
S. Beckwith for the Huble Ultra-Deep Field, NASA/ESA.
From Earth to the Universe
The immensity of the Cosmos
Looking into the globular cluster omega Centauri, gives you a feeling of the immensity of our Cosmos. As stated by Giordano Bruno in his book On Infinity: the Universe and the Worlds: “There are, thus, innumerable suns and an infinity of earths circling around those suns, in the same way our Earth circles around this Sun closer to us.”.
Looking into the globular cluster omega Centauri, gives you a feeling of the immensity of our Cosmos. As stated by Giordano Bruno in his book On Infinity: the Universe and the Worlds: “There are, thus, innumerable suns and an infinity of earths circling around those suns, in the same way our Earth circles around this Sun closer to us.”